Section 18 3 kingdoms and domains – Section 18: 3 Kingdoms and Domains sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. It delves into the intricate tapestry of life on Earth, exploring the three fundamental domains of life—Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya—and the six kingdoms that encompass them.
This comprehensive guide unravels the key characteristics that distinguish each domain and kingdom, providing a deep understanding of their evolutionary relationships and significance in the grand scheme of life’s diversity. Section 18 serves as a beacon, illuminating the path towards a deeper comprehension of the origins and interconnectedness of all living organisms.
Domains of Life
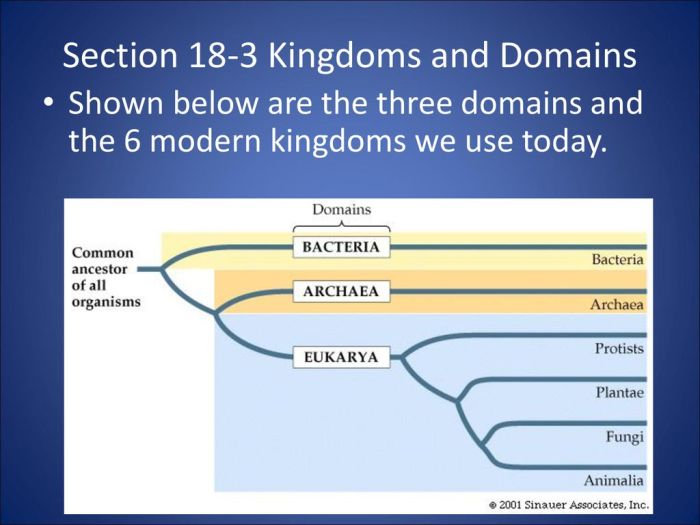
Life on Earth is incredibly diverse, ranging from microscopic bacteria to towering trees. Scientists have classified all living organisms into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Each domain is characterized by a unique set of structural, genetic, and metabolic features.
Bacteria
- Prokaryotic cells (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles)
- Small size (typically 0.5-5 micrometers)
- Peptidoglycan cell walls
- Circular DNA
- Diverse metabolic capabilities, including photosynthesis, respiration, and fermentation
Archaea
- Prokaryotic cells
- Similar size to bacteria
- Ether-linked cell membranes
- Circular DNA
- Extreme habitat preferences (e.g., hot springs, deep sea vents)
Eukarya, Section 18 3 kingdoms and domains
- Eukaryotic cells (with nucleus and membrane-bound organelles)
- Larger size (typically 10-100 micrometers)
- Cellulose or chitin cell walls (in plants and fungi, respectively)
- Linear DNA organized into chromosomes
- Complex metabolic pathways
Evolutionary Relationships
The three domains of life are believed to have evolved from a common ancestor. Bacteria and Archaea are more closely related to each other than to Eukarya, suggesting that Eukarya may have evolved from a symbiotic relationship between a bacterium and an archaeon.
Frequently Asked Questions: Section 18 3 Kingdoms And Domains
What is the significance of Section 18 in the National Science Education Standards?
Section 18 plays a crucial role in promoting the teaching of evolution in schools, emphasizing its importance in understanding the diversity of life on Earth.
How does the theory of evolution apply to the three domains of life?
The theory of evolution provides a framework for understanding the evolutionary relationships between the three domains of life, explaining their shared ancestry and the processes that have shaped their distinct characteristics.
What are the limitations of phylogenetic trees?
Phylogenetic trees are powerful tools for representing evolutionary relationships, but they have limitations, including the potential for errors due to incomplete data or methodological biases.