Delving into the intricacies of chemical bonding, the Stability in Bonding Worksheet Answer Key PDF emerges as an invaluable resource for students seeking a deeper understanding of this fundamental concept. This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of bond formation, stability, and the factors that govern these phenomena.
The worksheet delves into the diverse types of chemical bonds, encompassing ionic, covalent, metallic, and hydrogen bonds. Each bond type is meticulously examined, highlighting its unique characteristics and the interplay of electronegativity, bond length, bond order, and resonance in determining bond stability.
Stability in Bonding Worksheet

This worksheet aims to enhance students’ understanding of chemical bonding and its stability. It covers key concepts, such as types of bonds, bond strength, and factors affecting bond stability.
Through this worksheet, students will gain insights into the nature of chemical bonds, their characteristics, and the factors that influence their stability. This knowledge is essential for comprehending the behavior of atoms and molecules in various chemical reactions.
Bonding Concepts, Stability in bonding worksheet answer key pdf
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are several types of chemical bonds, each with unique characteristics and properties:
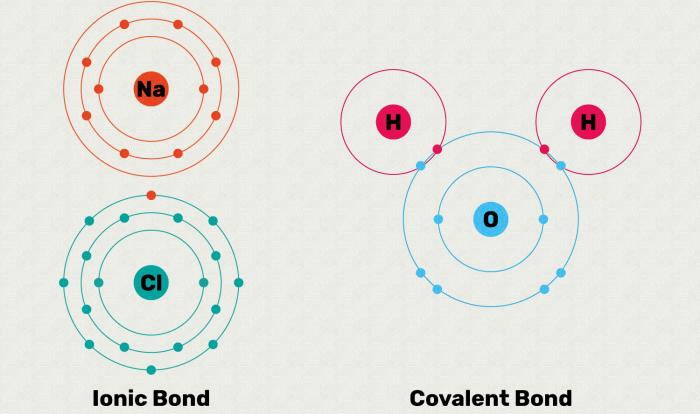
- Ionic Bonds: Formed between atoms with significant electronegativity differences. One atom donates electrons to another, resulting in the formation of oppositely charged ions that attract each other.
- Covalent Bonds: Formed when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, creating a strong bond.
- Metallic Bonds: Occur in metals, where valence electrons are delocalized and can move freely throughout the metal lattice. This electron sea holds the metal atoms together.
- Hydrogen Bonds: Weak interactions formed between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (such as N, O, or F) and another electronegative atom.
Bond strength is a measure of the energy required to break a bond. It is influenced by several factors, including bond length, bond order, and electronegativity.
Factors Affecting Bond Stability
The stability of a chemical bond is influenced by various factors:
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons. A higher electronegativity difference between bonded atoms leads to stronger ionic bonds and weaker covalent bonds.
- Bond Length: The distance between the nuclei of bonded atoms. Shorter bond lengths generally indicate stronger bonds.
- Bond Order: The number of electron pairs shared between bonded atoms. Double and triple bonds are stronger than single bonds due to the increased number of shared electrons.
- Resonance: The delocalization of electrons over multiple equivalent bonding structures. Resonance stabilizes bonds by distributing the electron density and reducing the overall energy of the molecule.
Question & Answer Hub: Stability In Bonding Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
What is the purpose of the Stability in Bonding Worksheet?
The worksheet aims to enhance students’ understanding of chemical bonding concepts, including bond types, bond strength, and factors affecting bond stability.
What types of chemical bonds are covered in the worksheet?
The worksheet covers various bond types, including ionic, covalent, metallic, and hydrogen bonds.
How is bond stability measured?
Bond stability is primarily measured by bond strength, which is influenced by factors such as electronegativity, bond length, bond order, and resonance.