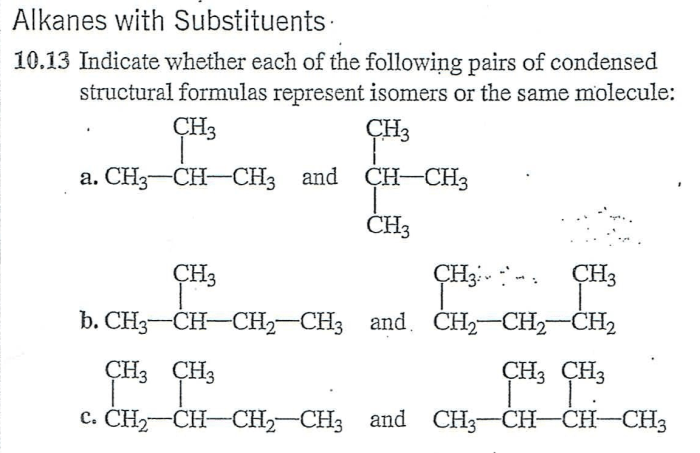
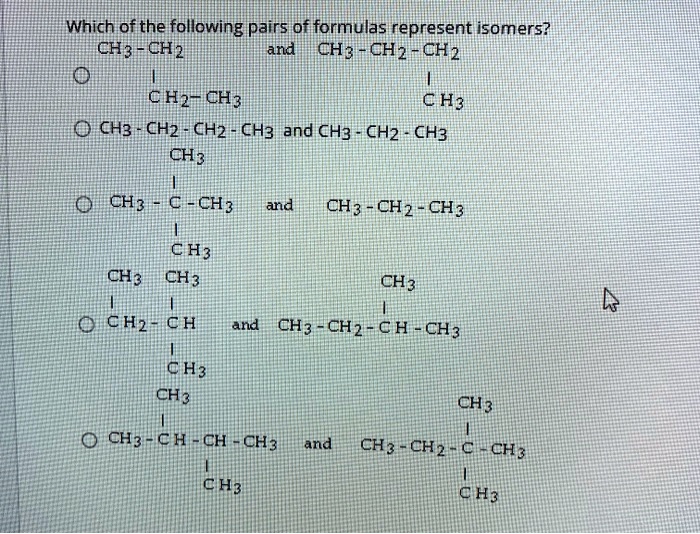
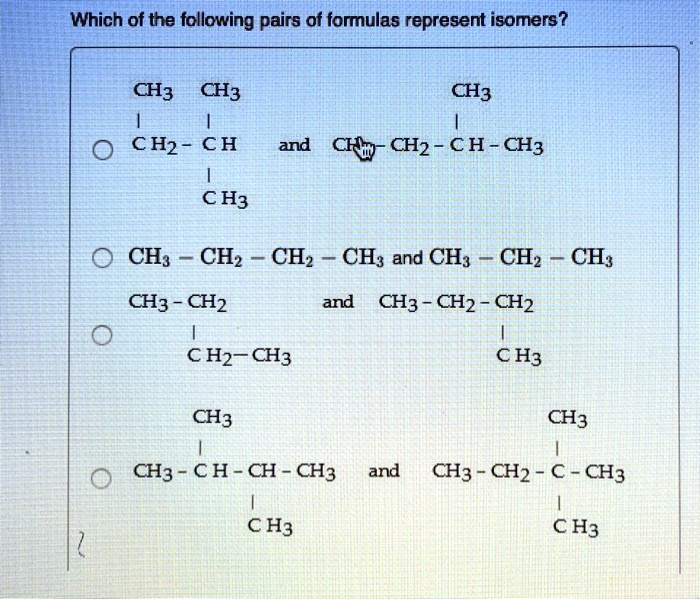
Which of the following pairs of formulas represent isomers? This question delves into the fascinating world of isomerism, where molecules with identical molecular formulas exhibit distinct structural arrangements, leading to unique properties and applications. Join us as we explore the concept of isomers, their diverse types, and the methods used to identify them.
Isomers play a crucial role in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. Understanding their behavior and properties is essential for comprehending the complexities of molecular interactions and their impact on the macroscopic world.
Isomers
Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. This means that they have the same number of atoms of each element, but the atoms are arranged in different ways.
There are two main types of isomers: structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers have different covalent bonding between the atoms, while stereoisomers have the same covalent bonding but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
Formula Representation of Isomers
Isomers can be represented using chemical formulas. The formula for an isomer shows the number of atoms of each element in the molecule, as well as the arrangement of the atoms.
For example, the molecular formula for butane is C 4H 10. However, there are two structural isomers of butane:
- n-butane: CH 3-CH 2-CH 2-CH 3
- isobutane: (CH 3) 3CH
The two isomers have the same molecular formula, but they have different structural formulas. This is because the atoms are arranged in different ways in the two isomers.
Methods for Identifying Isomers, Which of the following pairs of formulas represent isomers
There are a number of different methods that can be used to identify isomers. These methods include:
- Mass spectrometry: This method separates molecules based on their mass-to-charge ratio. Isomers will have the same mass-to-charge ratio, but they will have different fragmentation patterns.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: This method uses the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei to identify and characterize molecules. Isomers will have different NMR spectra because the atoms are arranged in different ways.
- Infrared (IR) spectroscopy: This method uses the absorption of infrared radiation to identify and characterize molecules. Isomers will have different IR spectra because the atoms are arranged in different ways.
Applications of Isomer Identification
Isomer identification is important in a number of different fields, including:
- Chemistry: Isomer identification is used to understand the structure and reactivity of molecules.
- Biology: Isomer identification is used to understand the structure and function of biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA.
- Medicine: Isomer identification is used to develop new drugs and to understand the metabolism of drugs.
Questions and Answers: Which Of The Following Pairs Of Formulas Represent Isomers
What are isomers?
Isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ in their structural arrangement.
How can we identify isomers?
Isomers can be identified using various methods, including spectroscopy, chromatography, and X-ray crystallography.
What are the different types of isomers?
There are two main types of isomers: structural isomers and stereoisomers.