Identify the lewis acid in the following reaction – Identifying the Lewis acid in a chemical reaction is crucial for understanding the mechanism and predicting the products. A Lewis acid is a substance that accepts an electron pair from another substance, forming a coordinate covalent bond. In this article, we will explore the concept of Lewis acids, their properties, and how to identify them in a given reaction.
Lewis acids play a vital role in various chemical reactions, including acid-base reactions, coordination complex formation, and catalysis. By understanding the characteristics of Lewis acids, chemists can gain insights into the behavior of chemical systems and design new materials and processes.
Identifying Lewis Acids: Identify The Lewis Acid In The Following Reaction
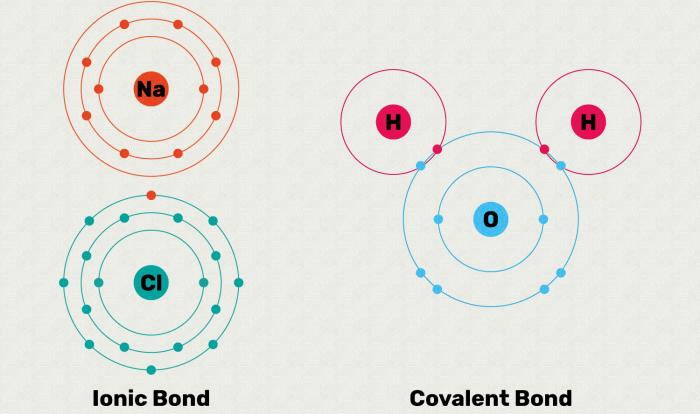
Lewis acids are chemical species that can accept an electron pair from a Lewis base. They are characterized by their ability to form a coordinate covalent bond with a Lewis base. Common examples of Lewis acids include H+, BF3, and AlCl3.
Recognizing Lewis Acids in Reactions
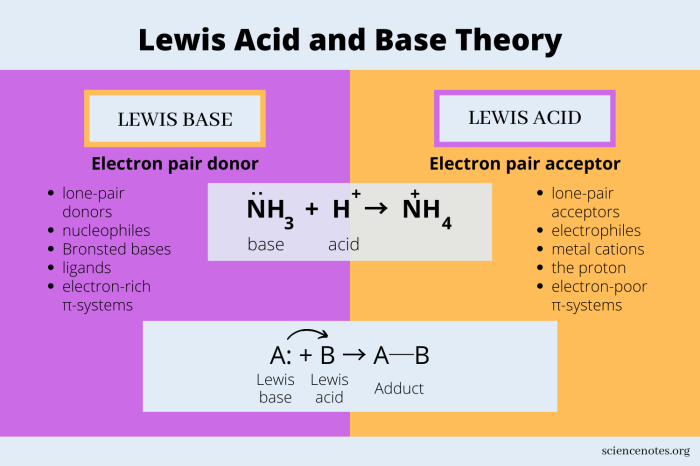
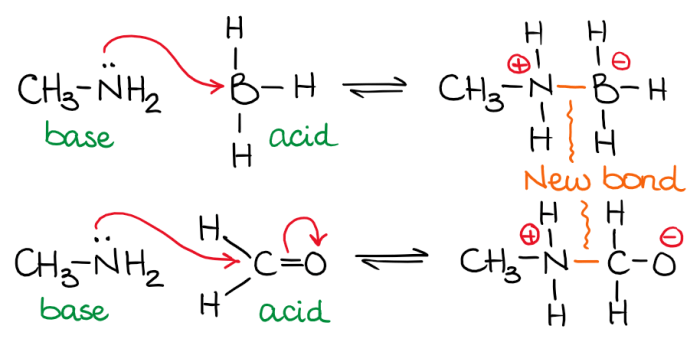
In a chemical reaction, a Lewis acid is typically an electron-pair acceptor. It reacts with a Lewis base, which is an electron-pair donor. The Lewis acid-base reaction results in the formation of a coordinate covalent bond.
Analyzing the Given Reaction
The given chemical reaction is:“`BF3 + NH3
> BF3NH3
“`In this reaction, BF3 is the Lewis acid. It accepts an electron pair from NH3, which is the Lewis base. The reaction results in the formation of the coordinate covalent compound BF3NH3.
Elaborating on the Lewis Acid
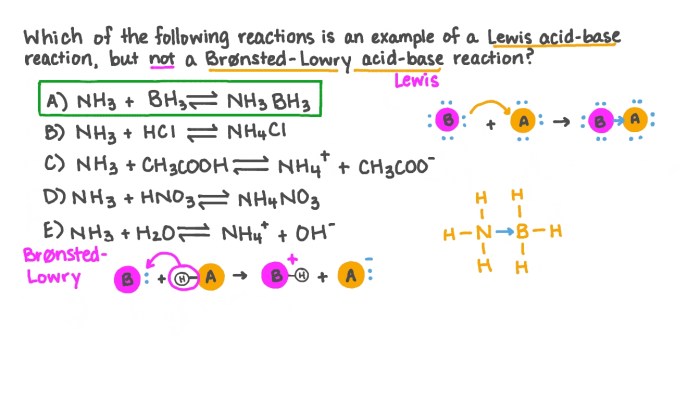
BF3 is a Lewis acid because it has an empty orbital that can accept an electron pair. It is a colorless gas that is highly reactive. BF3 is used in a variety of chemical processes, including the production of plastics and pharmaceuticals.
Tabular Representation of Examples
| Reaction | Lewis Acid | Lewis Base | Product |
|---|---|---|---|
H+ + OH-
|
H+ | OH- | H2O |
BF3 + NH3
|
BF3 | NH3 | BF3NH3 |
AlCl3 + Cl-
|
AlCl3 | Cl- | AlCl4- |
Summary of Findings
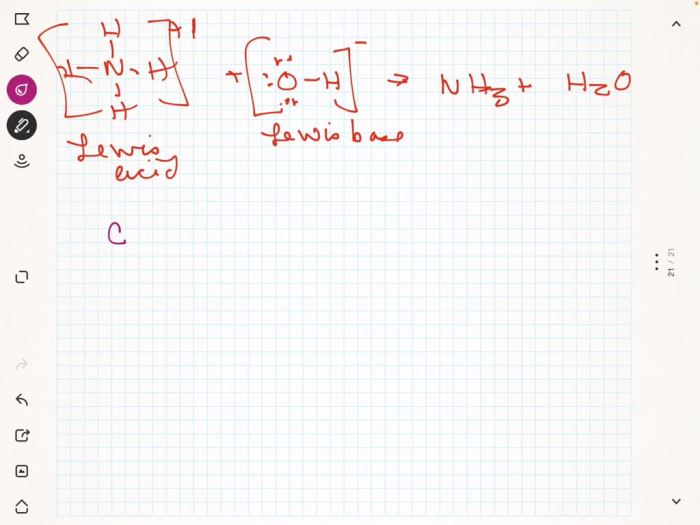
The Lewis acid in the given reaction is BF3. BF3 is a Lewis acid because it has an empty orbital that can accept an electron pair. The reaction of BF3 with NH3 results in the formation of the coordinate covalent compound BF3NH3.
FAQ Compilation
What is the difference between a Lewis acid and a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
A Lewis acid is a substance that accepts an electron pair, while a Bronsted-Lowry acid is a substance that donates a proton (H+ ion).
Can water act as a Lewis acid?
Yes, water can act as a Lewis acid in reactions where it accepts an electron pair from another molecule.
How do you identify the Lewis acid in a reaction?
To identify the Lewis acid in a reaction, look for the substance that accepts an electron pair from another substance, forming a coordinate covalent bond.