Explain the steps involved in providing an intermittent enteral feeding. – Intermittent enteral feeding, a crucial nutritional support method, plays a significant role in managing patients with compromised oral intake. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of intermittent enteral feeding, encompassing its purpose, methods, planning, equipment, administration, troubleshooting, monitoring, and evaluation.
By understanding the steps involved in intermittent enteral feeding, healthcare professionals can effectively implement this therapy, ensuring optimal patient outcomes and improving their quality of life.
Overview of Intermittent Enteral Feeding
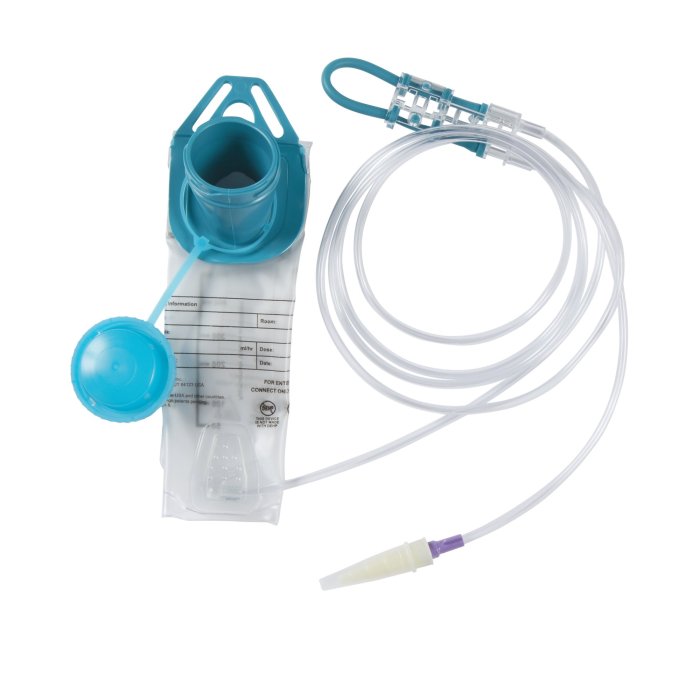
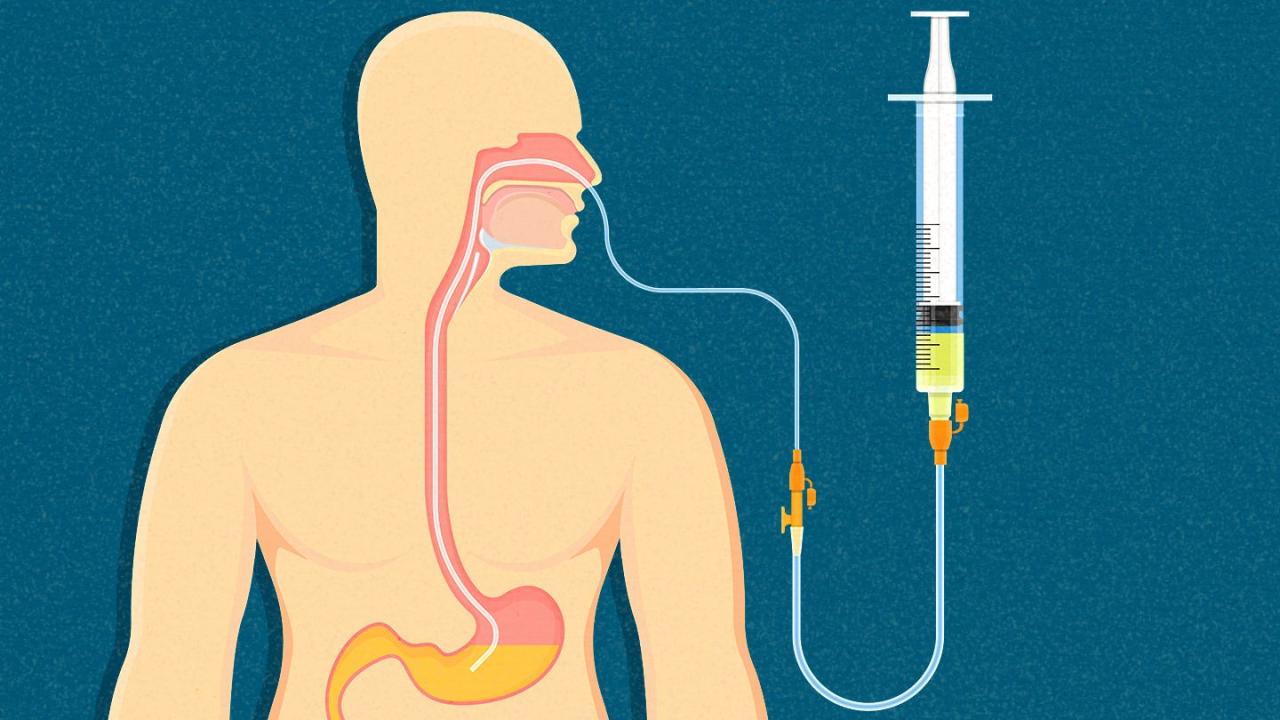
Intermittent enteral feeding (IEF) is a method of providing nutrition to patients who are unable to meet their nutritional needs orally. IEF involves administering liquid nutrition directly into the stomach or small intestine through a feeding tube. This method allows for controlled delivery of nutrients and fluids, ensuring adequate intake and preventing malnutrition.
IEF is often used in patients with:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Impaired gastrointestinal function
- Increased nutritional requirements
- Inability to tolerate oral intake for an extended period
There are different types of IEF methods, including:
- Bolus feeding: Delivering a large volume of formula over a short period
- Cyclic feeding: Administering formula in smaller volumes over a longer period
- Continuous feeding: Providing a continuous drip of formula over an extended period
Planning and Preparation
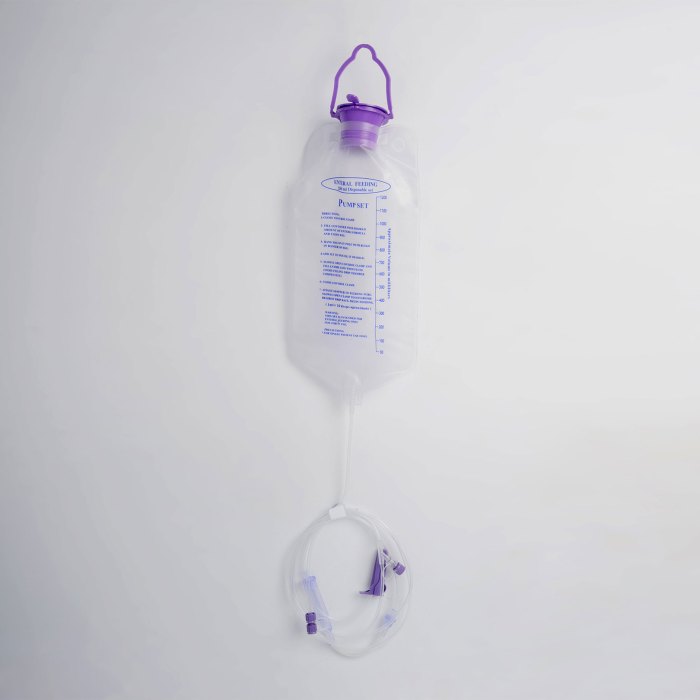
Planning and preparation are crucial for successful IEF. This involves:
- Identifying the patient’s nutritional needs and goals:Determining the patient’s calorie, protein, and fluid requirements based on their medical condition, activity level, and nutritional status.
- Determining the appropriate feeding formula and volume:Selecting a formula that meets the patient’s nutritional needs and is well-tolerated, and calculating the appropriate volume based on their nutritional requirements.
- Calculating the feeding rate and duration:Determining the rate at which the formula will be administered and the duration of each feeding session.
Equipment and Supplies: Explain The Steps Involved In Providing An Intermittent Enteral Feeding.
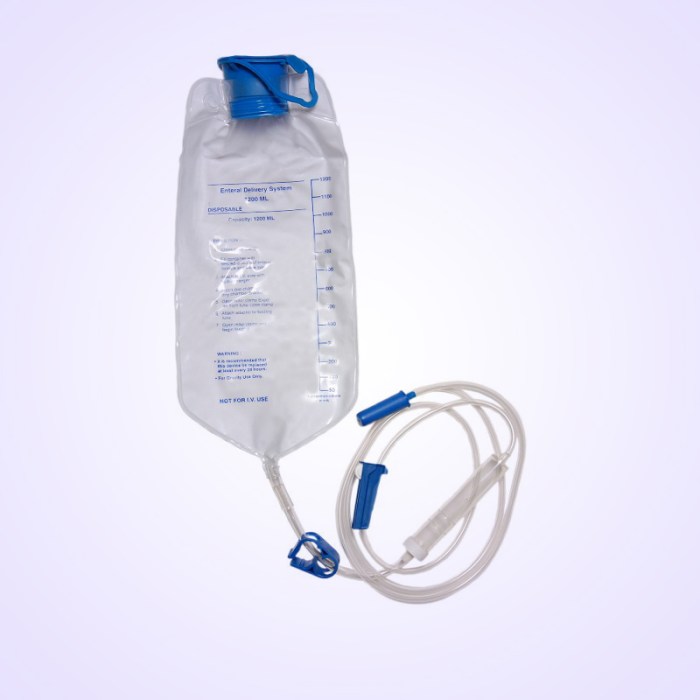
The following equipment and supplies are necessary for IEF:
- Feeding pump:A device that controls the flow rate and duration of feeding.
- Feeding bag:A container that holds the feeding formula.
- Feeding tube:A thin, flexible tube that is inserted into the patient’s stomach or small intestine.
- Syringe:A device used to administer medications or flush the feeding tube.
- Stethoscope:A device used to listen for bowel sounds before and during feeding.
- Gloves:To maintain sterility during feeding.
Proper use and maintenance of the equipment is essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of IEF.
Query Resolution
What are the benefits of intermittent enteral feeding?
Intermittent enteral feeding provides several benefits, including improved nutritional status, reduced risk of aspiration, enhanced patient comfort, and support for gastrointestinal function.
How is the appropriate feeding formula and volume determined?
The appropriate feeding formula and volume are determined based on the patient’s nutritional needs, medical condition, and tolerance. A registered dietitian or other qualified healthcare professional should make these determinations.
What are the common problems that may occur during intermittent enteral feeding?
Common problems that may occur during intermittent enteral feeding include feeding tube displacement, gastrointestinal intolerance, and electrolyte imbalances. Healthcare professionals should be vigilant in monitoring for these complications and implementing appropriate interventions.